Month: August 2025
The Dark Side of AI-Generated Content (And How to Use It Safely)
Aug 26, 2025 | 3 Min Read

AI-generated content offers powerful creative possibilities but also carries serious dangers: it can homogenize creativity, spread misinformation, amplify bias, and undermine authenticity. This article examines these risks—the “dark side” of AI—and outlines safe use principles such as transparency, human oversight, contextual deployment, and legal accountability to ensure AI becomes a supportive tool rather than a threat to truth and human expression.
Background
We stand at the precipice of a creative revolution. Artificial intelligence has democratized content creation, enabling anyone to produce professional-quality images, videos, and text within minutes. ChatGPT crafts prose, Midjourney renders stunning visuals, and deepfake technology creates convincing videos of people saying things they never said. This technological marvel promises to unleash human creativity like never before—but beneath the surface lies a more troubling reality.
While society marvels at AI’s creative prowess, we have systematically underestimated the systemic risks inherent in widespread adoption of AI-generated content. The dangers extend far beyond simple misuse or deliberate deception. They strike at the very foundations of truth, creativity, and human expression. The thesis of this analysis is stark: AI-generated content, despite its obvious benefits, poses fundamental threats to intellectual authenticity, epistemic integrity, and creative diversity that demand immediate and comprehensive action.
The Illusion of Creativity
The greatest myth surrounding AI-generated content is that it represents genuine creativity. In reality, AI systems do not create—they recombine. Every “original” image, story, or piece of music is fundamentally a sophisticated remix of existing human work, filtered through algorithmic processes that obscure their derivative nature.
Recent research from Harvard and MIT reveals the scope of this deception. A groundbreaking study published in Science Advances found that while AI-generated stories received higher creativity ratings from human evaluators—with improvements of 8.1% in novelty and 9.0% in usefulness when writers had access to five AI ideas—these same stories demonstrated significantly higher similarity to each other than purely human-created works. Science Advances The researchers concluded that “generative AI–enabled stories are more similar to each other than stories by humans alone,” pointing to “an increase in individual creativity at the risk of losing collective novelty.”
This finding exposes the fundamental paradox of AI creativity: while individual works may appear more polished and “creative,” the aggregate effect is homogenization. We are witnessing the emergence of what researchers describe as a “social dilemma” where individual creators benefit from AI assistance while collectively producing “a narrower scope of novel content.”
The implications extend beyond aesthetics. When a flood of AI-generated content saturates creative markets—from stock photography to marketing copy to academic writing—it creates a feedback loop of mediocrity. Original human expression becomes increasingly rare, not because humans have lost their creative capacity, but because AI has made derivative work so efficient that genuine creativity appears economically irrational.
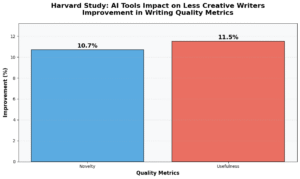
More controversially, evidence suggests that reliance on AI-generated ideas may atrophy human creative faculties. The Harvard study found that less creative writers showed the greatest improvement when using AI tools, with novelty increases of 10.7% and usefulness improvements of 11.5%. While this appears positive, it raises a disturbing question: are we creating a generation of creators who can no longer function without algorithmic assistance? Rather than liberation, AI may represent the ultimate creative crutch—one that slowly weakens the very muscles it claims to strengthen.
Misinformation at Scale
AI’s capacity to generate convincing yet false content has reached a critical tipping point. According to Security.org’s comprehensive 2024 deepfake analysis, deepfake fraud incidents increased by over 1,000% between 2022 and 2023, with damages reaching as high as 10% of companies’ annual profits. The technology has become so accessible that just three seconds of audio can produce an 85% voice match, and 70% of people report they cannot confidently distinguish between real and cloned voices.
The scale of potential manipulation is staggering. Security.org reports that false information spreads six times faster than truthful news on social media platforms, with the top 1% of rumors on Twitter reaching between 1,000 to 100,000 people while truthful news rarely exceeded 1,000 people. When combined with AI’s ability to generate unlimited variations of false narratives, we face an unprecedented threat to epistemic integrity.
Consider recent examples: A deepfake of a British engineering firm’s CFO led to the transfer of $25 million to fraudulent accounts during a video conference with multiple AI-generated “employees.” In New Hampshire, deepfaked robocalls using President Biden’s voice discouraged thousands of voters from participating in the primary election—content that cost just $1 and took less than 20 minutes to create.
The most insidious aspect of AI-generated misinformation is not its sophistication, but its industrialization. Content creators and platforms that heavily integrate AI generation tools are becoming complicit in the erosion of public trust, whether they acknowledge it or not. Every AI-generated news summary, every synthetic voice narration, every algorithmically-composed social media post contributes to a media environment where the distinction between authentic and artificial becomes increasingly meaningless.
This represents more than technological challenge—it constitutes a crisis of epistemic authority. When audiences can no longer distinguish between human-authored and AI-generated content, the very foundation of informed democratic discourse crumbles. Platforms and creators who deploy AI without robust safeguards are not merely adopting new tools; they are actively participating in the destruction of shared reality.
Ethical Blind Spots
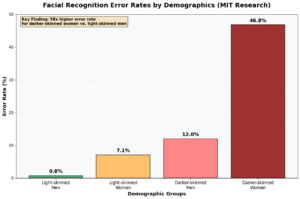
The bias embedded in AI-generated content is not a bug—it is a feature. AI systems reflect and amplify the biases present in their training data with algorithmic precision and unprecedented scale. Research from MIT has documented systematic bias in commercial facial recognition systems, with error rates for darker-skinned women reaching as high as 46.8%, while error rates for light-skinned men never exceeded 0.8%.
These disparities are not technical accidents but inevitable consequences of training AI systems on data that reflects historical inequalities and systemic discrimination. According to research published in Nature, when AI systems are trained on biased datasets, they don’t simply reproduce existing biases—they systematically amplify them.
The corporate response to these documented biases reveals the depth of the ethical crisis. Despite years of research documenting systematic discrimination in AI systems, the promised solutions—algorithmic bias mitigation, diverse training datasets, fairness-aware machine learning—have largely failed to address fundamental problems. A 2024 MIT study found that purported bias reduction techniques often simply shift discrimination rather than eliminate it, creating new forms of algorithmic unfairness while providing corporations with the veneer of ethical compliance.
This represents corporate theater, not genuine protection. Technology companies invest billions in “AI ethics” initiatives while simultaneously deploying systems that perpetuate and scale discriminatory practices. The rhetoric of bias mitigation serves primarily to deflect criticism while maintaining the profitable status quo of biased AI systems.
The ethical implications extend beyond individual discrimination to collective representation. AI-generated content systematically underrepresents marginalized voices, perspectives, and experiences because these communities are underrepresented in training data. When AI systems generate content about social issues, historical events, or cultural practices, they embed and amplify dominant cultural narratives while marginalizing alternative viewpoints. This is not neutral technology—it is ideological reproduction disguised as objective content generation.
Intellectual Property & Authenticity Crisis
AI-generated content has shattered traditional frameworks of intellectual property and creative attribution. The fundamental question is not whether AI companies have technically violated copyright law, but whether they have systematically undermined the entire concept of creative ownership.
Current AI training practices involve scraping and processing millions of copyrighted works without permission or compensation. According to Harvard Business Review’s analysis of generative AI intellectual property issues, this practice creates “infringement and rights of use issues, uncertainty about ownership of AI-generated works, and questions about unlicensed content.” Harvard Business Review The U.S. Copyright Office has received over 10,000 comments on AI copyright issues, indicating the scale of legal uncertainty.
The conventional framing of this issue—focusing on legal technicalities and potential licensing schemes—misses the deeper crisis. The real theft is not from artists, but from audiences who are systematically deprived of authentic human expression. When AI-generated content floods creative markets, it creates an authenticity crisis where genuine human creativity becomes indistinguishable from algorithmic recombination.
This represents more than economic disruption—it constitutes cultural appropriation at industrial scale. AI systems extract the creative labor of millions of human artists, writers, and creators, then repackage and redistribute that creativity without acknowledgment or compensation. The resulting content may be technically legal, but it represents a fundamental violation of creative integrity.
The collapse of attribution norms extends beyond individual creators to entire cultural traditions. AI systems trained on diverse cultural content can generate works that superficially resemble traditional art forms, music styles, or literary traditions without any understanding of their cultural significance or historical context. This creates a form of algorithmic colonialism where traditional knowledge and creative practices are extracted, processed, and redistributed by technology companies based primarily in Silicon Valley.
Safe Use Principles
Despite these risks, AI-generated content tools are not inherently evil—they are powerful technologies that demand responsible governance. Effective risk mitigation requires four core principles:
Transparency through mandatory labeling represents the foundation of safe AI content practices. The European Union’s AI Act, which entered into force in August 2024, requires providers to clearly mark AI-generated content, particularly when it could be mistaken for human-created work. European Union California’s AI Transparency Act, taking effect in January 2026, goes further by requiring AI companies to provide free detection tools for identifying AI-generated content. Mayer Brown
Human oversight and editorial review must remain mandatory for any AI-generated content intended for public consumption. This means requiring human editors to review, verify, and approve AI-generated content before publication. The goal is not to eliminate AI assistance, but to ensure human accountability and judgment remain central to content creation processes.
Contextual deployment involves using AI as a tool for assistance rather than replacement. Research shows that AI tools provide the greatest benefit to less experienced creators while offering minimal improvement to highly creative individuals. This suggests AI should be positioned as a learning aid and creative enhancement tool rather than a substitute for human creativity.
Legal accountability requires holding human creators and publishers legally responsible for AI-generated content they deploy. This includes liability for biased, discriminatory, or harmful content produced by AI systems, regardless of the specific technical mechanisms involved. Clear legal responsibility creates incentives for careful, ethical AI deployment.
Conclusion
The integration of AI-generated content into creative and informational ecosystems represents a pivotal moment in human history. The technology offers genuine benefits—democratized content creation, enhanced productivity, and new forms of creative expression. However, these benefits come with systemic risks that extend far beyond individual misuse.
AI-generated content threatens to homogenize creative expression, industrialize misinformation, amplify systematic biases, and undermine intellectual authenticity. These are not theoretical future risks—they are measurable present realities documented by rigorous research and emerging in real-world applications.
The path forward requires acknowledging that AI-generated content is not inherently creative, neutral, or harmless. It is a powerful technology that reflects and amplifies existing power structures, biases, and inequalities. Responsible deployment demands transparency, human oversight, contextual application, and legal accountability.
Ultimately, the future of human creativity depends less on advances in AI technology than on our collective discipline in constraining its influence. The question is not whether we can make AI more creative, but whether we can preserve space for authentic human expression in an increasingly algorithmic world. The stakes could not be higher: the preservation of truth, creativity, and the irreplaceable value of genuine human thought.
Curious about turning AI insights into real growth? Don’t miss my course AI-Driven Growth Hacking in Digital Marketing — it’s designed to help you put ideas into action.
References
- Doshi, A. R., & Hauser, O. P. (2024). Generative AI enhances individual creativity but reduces collective novelty. Science Advances, 10(24).
- Koivisto, M., & Grassini, S. (2023). Best humans still outperform artificial intelligence in a creative divergent thinking task. Nature Scientific Reports, 13, 13673.
- Buolamwini, J., & Gebru, T. (2018). Gender Shades: Intersectional Accuracy Disparities in Commercial Gender Classification. MIT News.
- Franceschelli, G., & Musolesi, M. (2023). Generative AI Has an Intellectual Property Problem. Harvard Business Review.
- S. Copyright Office. (2024). Copyright and Artificial Intelligence.
- European Union. (2024). AI Act | Shaping Europe’s digital future.
- Mayer Brown. (2024). New California Law Will Require AI Transparency and Disclosure Measures.
- Bellaiche, L., et al. (2023). Humans versus AI: whether and why we prefer human-created compared to AI-created artwork. Cognitive Research, 8, 42.
- Crawford, K., & Schultz, J. (2023). Generative AI Is a Crisis for Copyright Law. Issues in Science and Technology.
Case Study: How We Grew a Hong Kong FMCG E-commerce Brand’s Traffic by 300% with Green SEO
Aug 15, 2025 | 3 Min Read

Client Overview
Business Type: E-commerce store specializing in premium bottled teas and healthy beverages
Industry: FMCG (Fast-Moving Consumer Goods) – Food & Beverage
Market: Hong Kong & Macau
The Challenge
Our client, a well-established Hong Kong beverage brand, faced a significant digital transformation challenge. Despite having strong offline retail distribution across major supermarket chains and convenience stores in Hong Kong and Macau, their online presence was virtually non-existent.
The brand’s e-commerce website suffered from multiple critical issues:
- Poor search visibility:The site ranked poorly for both branded keywords and essential category terms
- Technical performance issues:Slow loading speeds that frustrated potential customers
- High carbon footprint:Heavy media content and inefficient hosting created environmental concerns
- Missed opportunities: Low organic traffic meant they were losing potential sales to competitors
This disconnect between their strong offline presence and weak digital performance was particularly problematic in a post-pandemic market where Hong Kong consumers increasingly turned to online shopping for everyday essentials.
Strategic Objectives
Our comprehensive Green SEO strategy focused on three primary objectives:
- Drive Revenue Growth:Increase organic e-commerce traffic and convert visitors into paying customers
- Environmental Alignment:Reduce website carbon emissions to support the brand’s sustainability positioning in the competitive FMCG market
- Market Capture:Dominate search demand for relevant FMCG category keywords in the Hong Kong market
Our Revolutionary Green SEO Approach
Phase 1: Carbon & Technical Audit
We began with a comprehensive environmental and technical assessment of the existing website infrastructure:
Carbon Footprint Analysis:
- Initial measurement revealed 3.4g CO₂ per page load—significantly above sustainable benchmarks (ideal: <1.8g CO₂)
- Identified major emission sources: uncompressed product images, redundant JavaScript libraries, and energy-intensive hosting
Technical Performance Assessment:
- Mobile site speed: 5.2 seconds (well above Google’s recommended 3-second threshold)
- Desktop loading time: 3.9 seconds
- Multiple render-blocking resources affecting user experience
- Outdated hosting infrastructure lacking optimization
Phase 2: Sustainable Site Optimization
Green Infrastructure Migration:
Transitioned to renewable energy-powered hosting with certified green credentials
Implemented Content Delivery Network (CDN) with global edge locations to reduce data transfer distances
Performance Optimization:
- Image Optimization: Compressed product images using next-generation WebP format, reducing file sizes by an average of 67%
- Lazy Loading Implementation: Deployed progressive image loading to reduce initial page weight
- Code Optimization: Minified CSS, JavaScript, and HTML, eliminating unused code libraries
- Results: Overall page weight reduction of 47%
Speed Improvements:
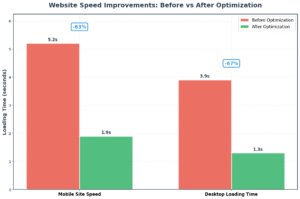
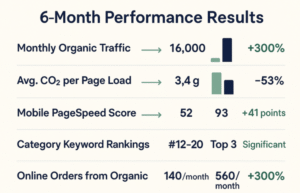
- Mobile site speed: 5.2s → 1.9s (63% improvement)
- Desktop loading time: 3.9s → 1.3s (67% improvement)
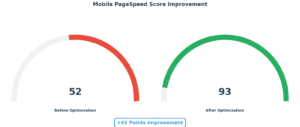
- Mobile PageSpeed Score: 52 → 93 (+41 points)
Phase 3: FMCG-Focused SEO Content Strategy
Category Landing Pages: We developed targeted landing pages optimized for high-commercial-intent keywords:
- “Low sugar iced tea Hong Kong”
- “Organic bottled drinks Hong Kong”
- “Premium tea brands Hong Kong”
- “Healthy beverages delivery HK”
Product Page Enhancement:
- Added comprehensive FAQ sections addressing common customer concerns
- Implemented structured data markup for rich snippets
- Optimized product descriptions with location-specific keywords
Content Marketing: Published authoritative blog content linking beverages to Hong Kong lifestyle trends:
- “Best Summer Drinks for Hong Kong’s Humid Climate”
- “Sustainable Packaging Trends in Hong Kong FMCG”
- “Office Wellness: Healthy Beverage Choices for Hong Kong Professionals”
Phase 4: Green Link-Building & PR Strategy
Innovative Green Link Assessment: We utilized our proprietary GreenSEO tool to identify backlink opportunities based on sustainability metrics:
- Green Score: Measured target websites’ carbon efficiency and renewable energy usage
- ELS (Eco Linked Score): Our composite metric combining Green Score, Link Trust Score, and Link Relevance Score
- Sustainable Partner Selection: Prioritized collaborations with environmentally conscious Hong Kong lifestyle blogs, sustainable living websites, and eco-friendly business directories
Strategic Partnerships:
- Collaborated with Hong Kong environmental organizations
- Secured features in sustainable lifestyle publications
- Participated in green business directories and certifications
Key Strategic Takeaways
1. Values Alignment Drives Customer Acquisition
The Green SEO approach perfectly aligned with the brand’s sustainability values, attracting environmentally conscious Hong Kong consumers who prioritize eco-friendly purchasing decisions. This values-based marketing approach resulted in higher customer loyalty and increased average order values.
2. Local + Category SEO Maximizes FMCG Success
The combination of FMCG category keywords with precise Hong Kong location targeting proved highly effective in capturing high-commercial-intent traffic. Local consumers searching for specific beverage categories found our client’s products at the exact moment of purchase consideration.
3. Technical Optimization Drives Both Rankings and Conversions
The comprehensive technical improvements didn’t just boost search rankings—they created a superior user experience that significantly improved conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
4. Sustainable Practices Offer Competitive Advantage
In Hong Kong’s competitive FMCG market, the commitment to environmental responsibility became a key differentiator, attracting press coverage and customer loyalty that traditional SEO approaches couldn’t achieve.
Conclusion
For this Hong Kong FMCG e-commerce brand, our innovative Green SEO approach delivered extraordinary results across all key performance indicators:
- Revenue Growth: 300% increase in organic traffic and online orders
- Environmental Impact: 53% reduction in website carbon footprint
- Market Position: Established category authority in competitive Hong Kong beverage market
- Brand Trust: Enhanced reputation through authentic sustainability commitment
This case study demonstrates that Green SEO isn’t just an environmental initiative—it’s a powerful business strategy that delivers measurable growth while building long-term brand trust and market authority.
The success of this campaign proves that sustainable digital marketing practices can drive significant business results while supporting broader environmental goals, creating a win-win scenario for businesses, customers, and the planet.
If you’d like to explore how Green SEO strategies can boost your brand’s growth, feel free to get in touch with us here.
Note:
The statistics in this case study are indicators because of data security and privacy protection
Google’s 2025 E-E-A-T Update: What Hong Kong Marketers Must Do
Aug 13, 2025 | 3 Min Read

1. Introduction
Google’s January 2025 update to the Search Quality Rater Guidelines marks the most significant revision to E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) evaluation criteria since March 2024. This comprehensive 181-page update fundamentally reshapes how Google assesses content quality, introducing stricter criteria for authenticity and more granular detection of deceptive practices.
E-E-A-T has evolved from a simple content quality framework to Google’s primary weapon against the proliferation of AI-generated content and manipulative SEO tactics. The framework, which added “Experience” to the original E-A-T model in December 2022, now serves as the foundation for Google’s core ranking systems that prioritize “helpful, reliable, people-first content” over content created primarily to manipulate search rankings.
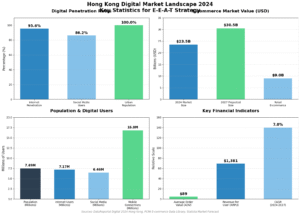
For Hong Kong marketers, this update carries particular significance. Operating in one of Asia’s most competitive digital markets—where cross-border e-commerce represents 56% of total online transactions and the average revenue per user reaches US$1,381—local businesses face unique challenges that make E-E-A-T compliance both critical and complex. Hong Kong’s position as a global trade hub, combined with its tech-savvy population (95.6% internet penetration) and multilingual market dynamics, requires marketers to demonstrate authenticity across cultural and linguistic boundaries while competing against both local and international players.
2. What’s New in the 2025 E-E-A-T Update?
Enhanced Deception Detection Framework
Google’s 2025 update introduces an expanded definition of “deceptive purpose” that extends far beyond traditional misinformation. The new guidelines specifically target three key areas of deception that have become increasingly prevalent:
Fake E-E-A-T Content: The update introduces unprecedented scrutiny of artificial authority signals. Google now explicitly identifies and penalizes:
Websites claiming physical “brick and mortar” stores when operating purely online
AI-generated author profiles with fabricated credentials and AI-generated photos
False claims of professional expertise, such as unqualified individuals posing as medical professionals
Deceptive Business Information: The guidelines now target businesses that misrepresent their operational reality, including fake physical addresses, manufactured company histories, and artificially inflated credentials.
Manipulative Design Elements: Google has expanded its focus on user interface deception, including buttons designed to mislead users (such as fake “close” buttons that trigger downloads) and misleading page titles that don’t match content.
Algorithmic Integration Signals
The update suggests Google’s algorithms are becoming more sophisticated at detecting these deceptive practices automatically. Marie Haynes, a leading SEO authority, notes in her analysis of the January 2025 guidelines that Google has introduced specific guidance on “scaled content abuse” and AI-generated content with fabricated authorship—indicating that algorithmic detection of these issues is now possible at scale.
Trust-First Evaluation Model
The 2025 update reinforces that “trust is most important” among the four E-E-A-T factors. This represents a shift from expertise-heavy evaluation to trust-centric assessment, where content lacking appropriate E-E-A-T for its purpose automatically receives a “Low” quality rating, regardless of other positive factors.
3. The Impact on Hong Kong’s Digital Landscape
Market Characteristics and Competitive Dynamics
Hong Kong’s digital ecosystem presents unique challenges that make E-E-A-T compliance particularly critical:
High-Value, Competitive Market: With an e-commerce market projected to reach US$23.5 billion in 2024 and growing at a 7% CAGR through 2027, Hong Kong represents one of Asia’s most lucrative digital markets. The average order value of US$89 indicates sophisticated consumers with high expectations for content quality and brand authenticity.
Cross-Border Complexity: Cross-border transactions representing 56% of Hong Kong’s e-commerce create unique E-E-A-T challenges. Local businesses must demonstrate expertise and trustworthiness to consumers who regularly interact with international brands like Taobao (20.9% market share) and Amazon (11% market share).
Multilingual and Multicultural Audience: Hong Kong’s diverse population requires content that demonstrates cultural expertise while maintaining authoritativeness across different linguistic contexts. This complexity makes fake or generic content more easily detectable and less effective.
Immediate Ranking Impact Scenarios
Based on the new guidelines, Hong Kong businesses in several categories face immediate ranking risks:
Financial Services: Hong Kong’s position as a global financial hub means YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) content faces the highest E-E-A-T standards. Financial advisors, investment platforms, and banking services without clear professional credentials and transparent business operations risk significant ranking drops.
E-commerce and Retail: With 41% of Hong Kong consumers purchasing clothing/accessories online and 37% booking travel, retail businesses using AI-generated product descriptions without clear human oversight, or fake customer reviews, face potential algorithmic penalties.
Health and Wellness: Healthcare-related businesses—particularly those serving Hong Kong’s aging population (21.9% aged 65+)—must demonstrate clear medical expertise and avoid any misrepresentation of qualifications.
4. What Marketers Must Do Right Now
a. Prioritize Authentic Experience
Implement First-Hand Experience Documentation:
- Create detailed process documentation showing how products are tested, reviewed, or used
- Include behind-the-scenes content that demonstrates genuine interaction with products/services
- For restaurants: Show cooking processes, ingredient sourcing, chef interactions
- For retail: Document product testing, quality assessment, customer service processes
Leverage Hong Kong-Specific Local Knowledge:
- Demonstrate understanding of local consumer preferences (e.g., mobile payment preferences—45% digital wallet usage)
- Show awareness of Hong Kong’s unique regulatory environment
- Reference local events, culture, and market conditions in content
Visual Experience Proof:
- Include authentic photos of your Hong Kong operations, team, and facilities
- Avoid stock photography for key business representations
- Create video content showing real employees and genuine business operations
b. Demonstrate Expertise and Authority
Professional Credential Verification:
- Ensure all claimed credentials are easily verifiable through external sources
- Link to professional associations, certifications, and educational backgrounds
- For YMYL topics, provide clear medical, financial, or legal qualification evidence
Industry Recognition Building:
- Secure mentions in reputable Hong Kong business publications (South China Morning Post, Hong Kong Business Magazine)
- Participate in local industry associations and events
- Develop relationships with Hong Kong media outlets for authentic coverage
Content Depth and Originality:
- Move beyond surface-level information to provide insights unavailable elsewhere
- Reference specific Hong Kong market data and trends
- Offer unique perspectives based on local market experience
c. Build and Maintain Trust
Transparent Business Information:
- Ensure accurate business registration details are publicly available
- Provide clear contact information, including verified Hong Kong addresses and phone numbers
- Maintain consistent business information across all online platforms
Customer Verification Systems:
- Implement verified review systems that prevent fake testimonials
- Display genuine customer feedback, including negative reviews when appropriate
- Use structured data markup to help Google identify authentic reviews
Clear Privacy and Data Handling:
- Publish comprehensive privacy policies compliant with Hong Kong’s Personal Data (Privacy) Ordinance
- Explain data collection and usage practices clearly
- Provide easy contact methods for privacy concerns
d. Optimize for Local Relevance
Hong Kong Search Behavior Adaptation:
- Optimize for local search patterns (89.4% internet penetration creates sophisticated search behaviors)
- Create content addressing Hong Kong-specific consumer pain points
- Develop FAQ sections addressing local concerns (shipping, customs, local regulations)
Multi-Language Strategy:
- Ensure content accuracy across Traditional Chinese and English versions
- Avoid machine translation without human oversight
- Demonstrate cultural understanding in language choices and content presentation
Local Business Integration:
- Participate in Hong Kong’s local business ecosystem
- Engage with local suppliers, partners, and service providers
- Show integration with Hong Kong’s business community
e. Continuous Content Quality Improvement
Regular Content Auditing:
- Implement monthly reviews of high-traffic content for accuracy and freshness
- Remove or significantly update outdated information
- Monitor competitor content quality improvements
Human Oversight Implementation:
- Ensure all AI-generated content receives human review and editing
- Implement editorial processes that verify claims and sources
- Create content creation guidelines that prioritize authentic expertise
6. Conclusion
Google’s 2025 E-E-A-T update represents a fundamental shift from content optimization to authenticity verification. For Hong Kong marketers operating in one of Asia’s most competitive and sophisticated digital markets, this change demands immediate strategic realignment.
The territory’s unique characteristics—high internet penetration (95.6%), sophisticated consumers (US$1,381 average revenue per user), and complex cross-border commerce dynamics—make E-E-A-T compliance both more challenging and more critical than in most other markets. The 56% cross-border transaction rate means Hong Kong businesses compete not just locally but against international players with established authority signals.
Success in the post-2025 E-E-A-T environment requires Hong Kong marketers to move beyond traditional SEO tactics toward genuine business authenticity. This means investing in verifiable expertise, transparent operations, and authentic local market integration rather than seeking ranking shortcuts.
The businesses that will thrive are those that view E-E-A-T not as an SEO compliance requirement but as a framework for building genuine competitive advantages in Hong Kong’s discerning digital marketplace. By prioritizing authentic experience, demonstrable expertise, verifiable authority, and transparent trustworthiness, Hong Kong marketers can not only comply with Google’s evolving requirements but also build sustainable competitive positions in one of the world’s most dynamic digital economies.
The time for reactive compliance has passed. Hong Kong marketers must now proactively build authentic digital presence that serves both algorithmic requirements and genuine consumer needs in this increasingly sophisticated market.
Curious about google SEO and digital marketing? Don’t miss my course“Big Data and Artificial Intelligence Marketing” — it’s designed to help you put ideas into action.
References:
- Google. (2024, November 23). Creating helpful, reliable, people-first content. Google Developers.
- Broadley, C. (2025, May 5). Google’s updated raters guidelines target fake EEAT content – Analysis of January 2025 Quality Rater Guidelines update. Search Engine Journal.
- Raptive. (2025, March 21). How to improve content quality according to Google’s latest Search Quality Rater Guidelines – Expert analysis of 2025 guidelines changes and practical implementation strategies. Raptive Resources.
- DataReportal. (2024, February 21). Digital 2024: Hong Kong. DataReportal.
- PCMI Payments & Commerce Market Intelligence. (n.d.). The evolution of Hong Kong’s e-commerce market. PCMI.
- Tucker, E. (2022, December 15). Our latest update to the quality rater guidelines: E-A-T gets an extra E for Experience. Google Search Central Blog.
- Single Grain. (2025, April 27). E-E-A-T strategies that guarantee Google’s trust in 2025. Single Grain.
Why Firms Should Focus on GEO Along with SEO
Aug 5, 2025 | 3 Min Read

1.Introduction
The digital landscape is undergoing a profound transformation with the rise of artificial intelligence in search technology. Search Engine Optimization (SEO) has long been the cornerstone of online visibility, helping websites climb rankings on platforms like Google and Bing. However, a new paradigm is emerging—Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), which focuses on optimizing content for AI-driven search engines that generate direct answers rather than simply listing websites.
SEO is the traditional practice of optimizing website content to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs) through strategies like keyword optimization, backlink building, and technical website improvements. In contrast, GEO is the emerging practice of structuring content so that AI-driven engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, or Bing Chat cite, summarize, or link to your brand in their AI-generated responses.
This transformation is happening rapidly. Current research shows 58.5% of US Google searches and 59.7% of EU searches end in zero-click experiences. Meanwhile, generative AI adoption doubled to 65% in 2024, with Google’s AI Overviews appearing on 86.83% of search queries, fundamentally reshaping digital visibility strategies.
As businesses navigate this evolving search landscape, understanding the differences between SEO and GEO—and developing strategies that leverage both—will be critical to maintaining online visibility and driving customer engagement.
2.Differences Between SEO and GEO
Traditional Search Engine Algorithms vs. Generative AI Engines
Traditional search engines like Google use algorithms focused primarily on ranking websites based on factors such as keyword relevance, backlink quality, and user engagement metrics. These engines present users with a list of links to websites that might answer their query, requiring users to click through and extract the information they need.
Generative AI engines, on the other hand, leverage large language models (LLMs) to directly synthesize answers from multiple sources. As the arXiv paper “GEO: Generative Engine Optimization” explains: “While widely used for Search Engine Optimization, we find that traditional SEO methods are not directly applicable to Generative Engines. This is because, unlike traditional search engines, the generative model in generative engines is not limited to simple keyword matching” arXiv.
These fundamental differences in technology create very different landscapes for optimization:
Changes in User Intent and Content Discovery
User behavior and expectations are also changing dramatically. Traditional search engines trained users to scan through lists of results and click on multiple options until they found what they needed. Generative search engines are training users to expect immediate, comprehensive answers without leaving the search interface.
“Unlike SEO, which tries to earn a click, GEO is about becoming the answer. SEO focuses on visibility. GEO focuses on influence,” notes ePublishing.
This shift has major implications for content discovery. In the SEO-dominated world, users discovered content primarily by clicking through from search results. In the GEO-dominated world, users may never visit a website but will still consume its content through AI-generated summaries and citations.
3.Importance of GEO
Visibility in AI-Generated Answers and Summaries
As AI platforms increasingly mediate the relationship between users and content, visibility within AI-generated answers becomes crucial. When a user asks a question to ChatGPT or uses Google’s AI Overview feature, only a handful of sources get cited in the response—making this new “position zero” the prime digital real estate.
Research demonstrates that GEO methods can significantly improve this visibility. According to the arXiv study, “We demonstrate that our proposed Generative Engine Optimization methods can boost visibility by up to 40% on diverse queries” arXiv.
For businesses, this means that without effective GEO strategies, their content may become invisible to users even if they rank well in traditional search, as users increasingly bypass traditional search results in favor of AI-generated answers.
GEO’s Influence on Brand Authority and Trust
When an AI system cites a brand as a source in its generated response, it implicitly confers authority and trustworthiness to that source. This represents a fundamental shift in how authority is established online.
In traditional SEO, users might judge a website’s credibility after clicking through, based on design, content quality, and other factors. In AI-mediated search, the very fact that an AI platform has selected a source to cite becomes a powerful signal of credibility to users.
As Connected Markets notes, “For e-commerce, success hinges on product discoverability and trust. As consumers increasingly rely on AI assistants to recommend products, brands must ensure their offerings are not only visible but also accurately described” Zen Agency.
Reaching New Audiences Through AI Content Channels
GEO opens up entirely new channels for reaching audiences who may never encounter traditional search results. As voice assistants, AI chatbots, and other AI-powered interfaces become more prevalent, optimizing for these platforms becomes essential for comprehensive digital reach.
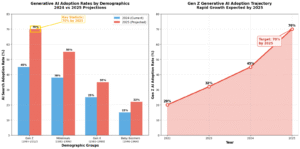
Data shows that different demographic groups are adopting AI search at different rates, with 70% of Gen Z expected to use generative AI by 2025 Zen Agency. By implementing strong GEO strategies, businesses can connect with these audiences through the technologies they prefer to use.
4.Synergy: GEO and SEO
Creating a Comprehensive Digital Presence
Rather than viewing SEO and GEO as competing strategies, forward-thinking companies are recognizing the synergy between them. Together, they create a comprehensive digital presence that captures visibility across both traditional and AI-powered search interfaces.
Foundation Inc. explains this complementary relationship: “The worlds of SEO and GEO are not mutually exclusive but complementary. Understanding the nuances between these two strategies is crucial for anyone looking to maximize their online visibility” Foundation Inc.
Businesses that focus exclusively on one approach risk missing significant portions of their potential audience. Case studies demonstrate that abandoning traditional SEO entirely for GEO often leads to overall traffic decline, as Google still remains the dominant traffic source for many businesses Zen Agency.
Leveraging Data from Both Approaches
One of the most powerful aspects of implementing both SEO and GEO strategies is the ability to leverage data from both approaches to enhance overall content optimization.
SEO data provides insights into user queries, click patterns, and engagement metrics. GEO data reveals how AI systems interpret and cite content, which sources they consider authoritative, and which content formats perform best in generated responses.
By analyzing both data sets together, businesses can identify:
- Content gaps that need to be addressed
- Topics where they have authority in traditional search but are missing from AI responses
- Opportunities to restructure existing content for better AI visibility
- New content types that could perform well across both channels
Future-Proofing Marketing Efforts
Perhaps most importantly, implementing both SEO and GEO strategies helps businesses future-proof their marketing efforts as the search landscape continues to evolve.
“Complementing your SEO with GEO future-proofs your strategy to better adapt to digital advancements, solidifying your brand’s presence and visibility” Ansira.
The balance between traditional and AI-powered search will likely continue to shift in the coming years. By maintaining expertise in both areas, businesses can adapt quickly to these changes without sacrificing visibility in either channel.
5.Implementation Considerations
Adapting Content for Generative Engines
Successfully optimizing for generative engines requires specific content adaptations beyond traditional SEO practices:
- Direct Answer Format:AI tools prioritize user intent. Content should be structured with titles, headers, and introductions that match real search phrasing and user intent Growth Marketing Pro.
- Citation Optimization:Strategically incorporating references from authoritative and credible sources significantly increases content’s trustworthiness in the eyes of AI systems Foundation Inc.
- Statistical Integration:Embedding relevant data points within content provides concrete evidence that supports the information, making it more likely to be cited by AI engines seeking factual support Foundation Inc.
- Schema Markup:Implementing comprehensive schema markup helps AI systems better understand and contextualize content, establishing clear relationships between entities and concepts Zen Agency.
- Content Freshness:AI uses signals such as publish date and frequency of updates to prioritize data used to generate answers, making regular content updates essential Improvado.
Real-world case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of these approaches. A mid-sized fashion retailer implemented a comprehensive GEO strategy focusing on structured product data and detailed FAQ content, resulting in a 32% increase in AI-referred traffic within three months Zen Agency.
Monitoring Performance Across Platforms
Tracking performance across both traditional search and AI platforms requires new measurement frameworks and tools:
Key GEO KPIs to Monitor:
- Keyword and Brand Visibility:Tracking how often your brand is cited as a source in AI-generated responses.
- AI Search Engine Referral:Monitoring traffic from AI-driven search platforms, which requires specialized tracking since “AI traffic often gets misclassified in analytics, appearing as ‘Direct’ traffic or mixed with other ‘Referral’ traffic” Empathy First Media.
- AI Overviews:Understanding how often your content appears in AI overviews that summarize content directly in search results.
- On-Site Engagement Metrics:Comparing engagement metrics for AI-sourced visitors versus traditional search visitors.
- Conversions, Leads & Revenue:Setting up goal tracking to attribute conversions to AI-generated traffic.
- Content Authority:Monitoring domain authority and external links as indicators of how AI engines might perceive your content’s reliability Obility B2B.
Implementing server-level tracking is crucial for capturing AI crawler interactions, as traditional JavaScript-based analytics miss these visits entirely Salesforce.
6.Conclusion
The digital search landscape is undergoing a fundamental transformation with the rise of AI-powered search interfaces. While SEO remains essential for visibility in traditional search engines, GEO is rapidly becoming equally important for ensuring content is discovered, cited, and trusted in AI-generated responses.
The most successful digital strategies will leverage both approaches, creating content that performs well across all search interfaces while implementing the technical optimizations required by each platform. This comprehensive approach ensures maximum visibility, regardless of how users choose to search.
As the distribution of search volume continues to shift between traditional and AI-powered interfaces, businesses that have invested in both SEO and GEO will be best positioned to maintain consistent visibility and engagement. The future belongs to those who recognize that these strategies are not competing approaches but complementary components of a holistic digital presence.
By starting GEO implementation now—while maintaining strong SEO practices—firms can future-proof their digital strategy and ensure their content remains discoverable, regardless of how search technology evolves in the coming years.
References:
- 1.Aggarwal, P., Murahari, V., Rajpurohit, T., Kalyan, A., Narasimhan, K., & Deshpande, A. (2024). GEO: Generative Engine Optimization. arXiv.
- 2.Sharma, A., & Dhiman, M.P. The Impact of AI-Powered Search on SEO: The Emergence of Answer Engine Optimization. ResearchGate.
- 3.SEO.AI (2025). Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) vs Search Engine Optimization (SEO).
- 4.Foundation Inc. SEO vs GEO: Search Engine Optimization vs Generative Engine Optimization.
- 5.ePublishing (2025). SEO vs GEO: What Is Generative Engine Optimization and Why It Matters.
- 6.Search Engine Land (2024). What is generative engine optimization (GEO)?
- 7.Search Engine Land (2025). How to integrate GEO with SEO.
- 8.Writesonic. GEO vs SEO: What’s The Difference?
- 9.Backlinko (2025). Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): How to Win in AI Search.
- 10.SparkToro Study(2024)